This is the readme.txt for the model associated with the paper
(1) Wang YJ, Sung RJ, Lin MW, Wu SN. Contribution of BK(Ca)-channel
activity in human cardiac fibroblasts to electrical coupling of
cardiomyocytes- fibroblasts. J Membr Biol 2006;213:175-185.
(2) Luo CH, Rudy Y. A dynamic model of the cardiac ventricular action
potential. II. Afterdepolarizations, triggered activity, and
potentiation. Circ Res 1994;74:1097-1113.
Abstract:
Cardiac fibroblasts are involved in the maintenance of myocardial
tissue structure. However, little is known about ion currents in human
cardiac fibroblasts. It has been recently reported that cardiac
fibroblasts can interact electrically with cardiomyocytes through gap
junctions. Ca(2+)- activated K(+) currents (I (K[Ca])) of cultured
human cardiac fibroblasts were characterized in this study. In
whole-cell configuration, depolarizing pulses evoked I (K(Ca)) in an
outward rectification in these cells, the amplitude of which was
suppressed by paxilline (1 microM) or iberiotoxin (200 nM). A
large-conductance, Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK(Ca)) channel with
single-channel conductance of 162 +/- 8 pS was also observed in human
cardiac fibroblasts. Western blot analysis revealed the presence of
alpha- subunit of BK(Ca) channels. The dynamic Luo-Rudy model was
applied to predict cell behavior during direct electrical coupling of
cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts. In the simulation,
electrically coupled cardiac fibroblasts also exhibited action
potential; however, they were electrically inert with no
gap-junctional coupling. The simulation predicts that changes in gap
junction coupling conductance can influence the configuration of
cardiac action potential and cardiomyocyte excitability. I(K(Ca)) can
be elicited by simulated action potential waveforms of cardiac
fibroblasts when they are electrically coupled to cardiomyocytes. This
study demonstrates that a BK(Ca) channel is functionally expressed in
human cardiac fibroblasts. The activity of these BK(Ca) channels
present in human cardiac fibroblasts may contribute to the functional
activities of heart cells through transfer of electrical signals
between these two cell types.
-------
To run the models:
XPP: start with the command
xpp ode\LRd01.ode
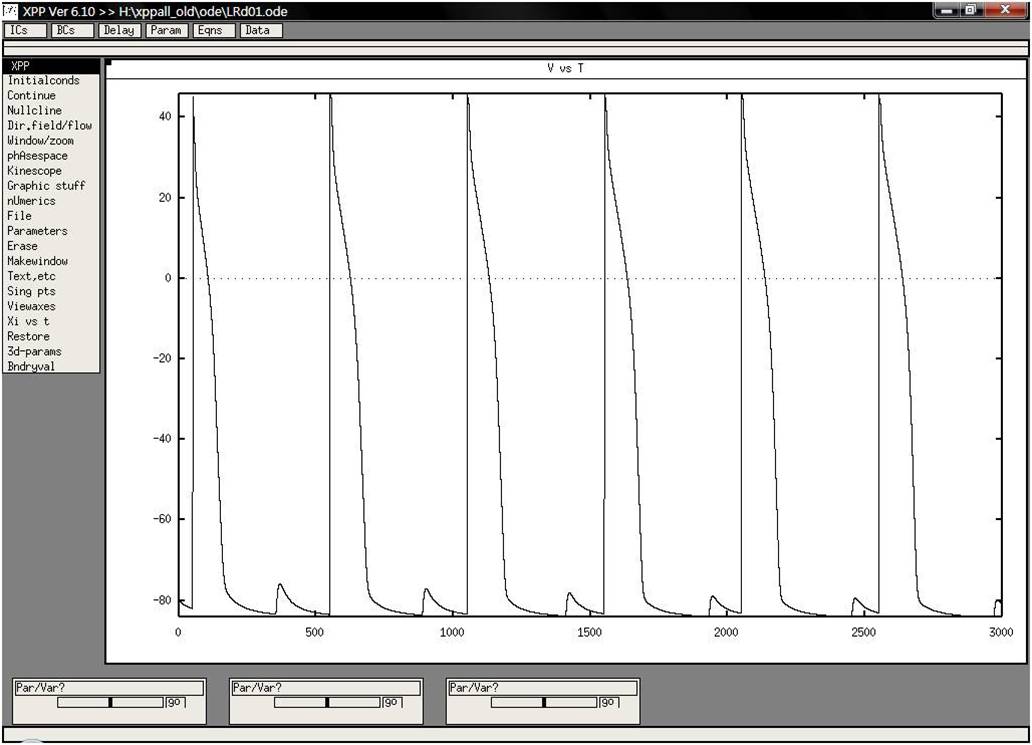
To press (I)nitial and (L)ast 3-4 times, then change parameter (Par)
period from 200 to 500 msec. Delayed after-depolarization shown in
attached figure along with triggered activity will emerge.
An author supplied image of the model run:
 Bard Ermentrout's website http://www.pitt.edu/~phase/ describes how to
get and use xpp.
These model files were submitted by:
Sheng-Nan Wu
Department of Physiology
National Cheng Kung University Medical College
Tainan City 70101, Taiwan
snwu@mail.ncku.edu.tw
Bard Ermentrout's website http://www.pitt.edu/~phase/ describes how to
get and use xpp.
These model files were submitted by:
Sheng-Nan Wu
Department of Physiology
National Cheng Kung University Medical College
Tainan City 70101, Taiwan
snwu@mail.ncku.edu.tw
 Bard Ermentrout's website http://www.pitt.edu/~phase/ describes how to
get and use xpp.
These model files were submitted by:
Sheng-Nan Wu
Department of Physiology
National Cheng Kung University Medical College
Tainan City 70101, Taiwan
snwu@mail.ncku.edu.tw
Bard Ermentrout's website http://www.pitt.edu/~phase/ describes how to
get and use xpp.
These model files were submitted by:
Sheng-Nan Wu
Department of Physiology
National Cheng Kung University Medical College
Tainan City 70101, Taiwan
snwu@mail.ncku.edu.tw