Effects of pipette tip and membrane patch geometry on GABAa-mediated
currents, in patch-clamp experiments
--------------------------------------------------------------------
January 31st 2011 - Michele Giugliano, PhD
Ion currents, mediated by GABAa-receptors in outside-out membrane
patches, may alter the concentration of Chloride ions inside the
pipette and the membrane patch. GABAa-receptors are in fact
ionotropic synaptic receptors, selective to Chloride ions. Therefore,
chloride fluxes across the membrane patch correlate to GABAa-receptor
opening. Chloride ions accumulation, depletion and diffusion, inside
the pipette and the membrane patch, affect by definition the Chloride
equilibrium (i.e. Nernst) electrical potential. This in turn changes
the ionic driving force underlying GABAa-mediated currents. It
follows that, in case of very small volumes and confined geometries,
voltage-clamp recordings of GABAa- receptor currents carry information
on both i) Chloride diffusion and ii) receptor kinetics.
The relevance of (i) and (ii) have been studied numerically by
defining a 1-dimensional biophysical model, released here to the
interested user.
The model refers to the manuscript:
Mirko Moroni, Istvan Biro, Michele Giugliano, Ranjit Vijayan, Philip
C. Biggin, Marco Beato, and Lucia G. Sivilotti. Chloride Ions in the
Pore of Glycine and GABA Channels Shape the Time Course and Voltage
Dependence of Agonist Currents. J Neuroscience 2011
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Model description:
Refer to the original paper Method section, as well as to its
Supplemental Materials, for a complete model description.
Very briefly, a 1-dimensional diffusion equation has been complemented
by appropriate boundary conditions, accounting for a multi-taper
conical pipette and a simplified outside-out membrane-patch
geometry. This equation simulates Chloride ion diffusion inside the
pipette very tip and in proximity to the membrane-patch, determining
at each time-step the actual Chloride concentration. Outside the
membrane-patch, the Chloride concentration is assumed to be fixed and
set to a bulk value. A reduced model of ligand-gated ohmic ion
current density has been then coupled to the simulation of Chloride
diffusion, making it possible to account for 1) depletion or
accumulation of Chloride in response to opening of GABAa receptors, as
well as for 2) changes in the Chloride reversal potential and ion
current driving force.
The full model has been implemented in MATLAB, by an implicit scheme
for unconditional numerical stability, and a systematic parameters
exploration has been carried out on a large university computer
cluster.
Code description:
The source code released here, refers to a full-working demo that can
be employed for replicating the paper results and for extending its
analysis. It is invoked by changing the current working directory to
the folder where the package has been uncompressed (e.g. cd
MyDocuments/ModelDB) and then typing "main" at the MATLAB prompt. The
code is extensively commented and should be self-explicative, in
addition to the information provided by the paper as main text and
supplemental material.
main.m : is the main routine that should be invoked and that should be
studied.
It calls matlab/set_parameters.m that sets the numerical
values of each parameter.
It calls matlab/simulation_step.m that performs a single
temporal iteration step, solving for the concentration
vector.
At the end of the computation, the script displays the results as a
plot related to Figure 3 in the paper, composed by two panels:
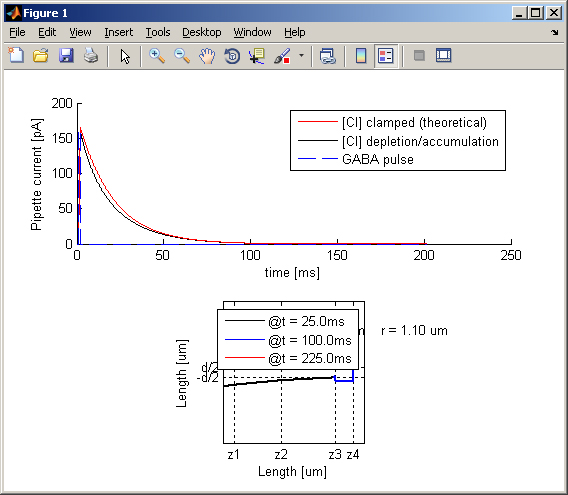
 They report the actual temporal profile of the GABAa-receptors
mediated ion current, recorded by the virtual pipette, comparing the
effect of Chloride diffusion to the theoretical prediction (i.e. the
voltage-clamp current profile expected from the kinetic properties of
the GABAa-receptors activation and deactivation alone). A snapshot of
the spatial concentration profile of Chloride at three different
moments in time (i.e. at the beginning of the simulation, during the
simulated GABA pulse, and at the end of the simulation). The script
also invokes the following command, before finishing and returning the
control to the user:
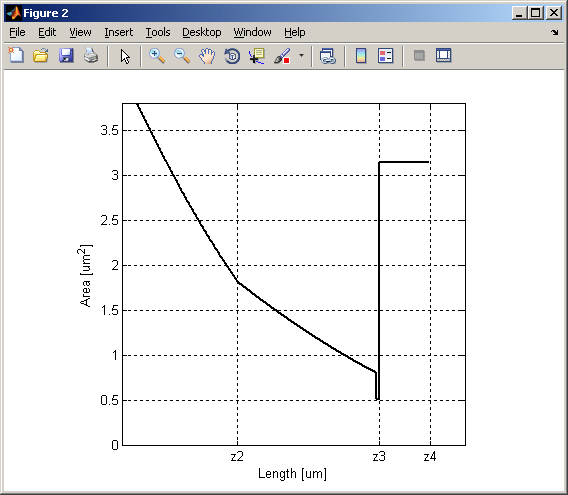
matlab/plot_free_area_testing.m : is provided for testing and
demonstration purposes. It plots the
actual model geometry and the free
passage area through the pipette and
omega-shaped patch..
Interested users should start studying the code of main.m and
simulation_step.m.
Antwerp, Jan 31st 2011, Michele Giugliano PhD
(michele.giugliano@ua.ac.be)
They report the actual temporal profile of the GABAa-receptors
mediated ion current, recorded by the virtual pipette, comparing the
effect of Chloride diffusion to the theoretical prediction (i.e. the
voltage-clamp current profile expected from the kinetic properties of
the GABAa-receptors activation and deactivation alone). A snapshot of
the spatial concentration profile of Chloride at three different
moments in time (i.e. at the beginning of the simulation, during the
simulated GABA pulse, and at the end of the simulation). The script
also invokes the following command, before finishing and returning the
control to the user:
matlab/plot_free_area_testing.m : is provided for testing and
demonstration purposes. It plots the
actual model geometry and the free
passage area through the pipette and
omega-shaped patch..
Interested users should start studying the code of main.m and
simulation_step.m.
Antwerp, Jan 31st 2011, Michele Giugliano PhD
(michele.giugliano@ua.ac.be)

 They report the actual temporal profile of the GABAa-receptors
mediated ion current, recorded by the virtual pipette, comparing the
effect of Chloride diffusion to the theoretical prediction (i.e. the
voltage-clamp current profile expected from the kinetic properties of
the GABAa-receptors activation and deactivation alone). A snapshot of
the spatial concentration profile of Chloride at three different
moments in time (i.e. at the beginning of the simulation, during the
simulated GABA pulse, and at the end of the simulation). The script
also invokes the following command, before finishing and returning the
control to the user:
matlab/plot_free_area_testing.m : is provided for testing and
demonstration purposes. It plots the
actual model geometry and the free
passage area through the pipette and
omega-shaped patch..
Interested users should start studying the code of main.m and
simulation_step.m.
Antwerp, Jan 31st 2011, Michele Giugliano PhD
(michele.giugliano@ua.ac.be)
They report the actual temporal profile of the GABAa-receptors
mediated ion current, recorded by the virtual pipette, comparing the
effect of Chloride diffusion to the theoretical prediction (i.e. the
voltage-clamp current profile expected from the kinetic properties of
the GABAa-receptors activation and deactivation alone). A snapshot of
the spatial concentration profile of Chloride at three different
moments in time (i.e. at the beginning of the simulation, during the
simulated GABA pulse, and at the end of the simulation). The script
also invokes the following command, before finishing and returning the
control to the user:
matlab/plot_free_area_testing.m : is provided for testing and
demonstration purposes. It plots the
actual model geometry and the free
passage area through the pipette and
omega-shaped patch..
Interested users should start studying the code of main.m and
simulation_step.m.
Antwerp, Jan 31st 2011, Michele Giugliano PhD
(michele.giugliano@ua.ac.be)