***********************************************************************
Simulation code from Hass, Hertaeg and Durstewitz (2016), "A detailed,
data data-driven network model of prefrontal cortex reproduces key
features of in vivo activity", PLoS Comput Biol
***********************************************************************
This package should provide all files needed to simulate the network
model introduced in the paper above. Run the simulation with 1000
neurons for 1000 ms using the script 'RunIDNet.m'.
This default simulation completes in a minute or two and should
display a graph like:
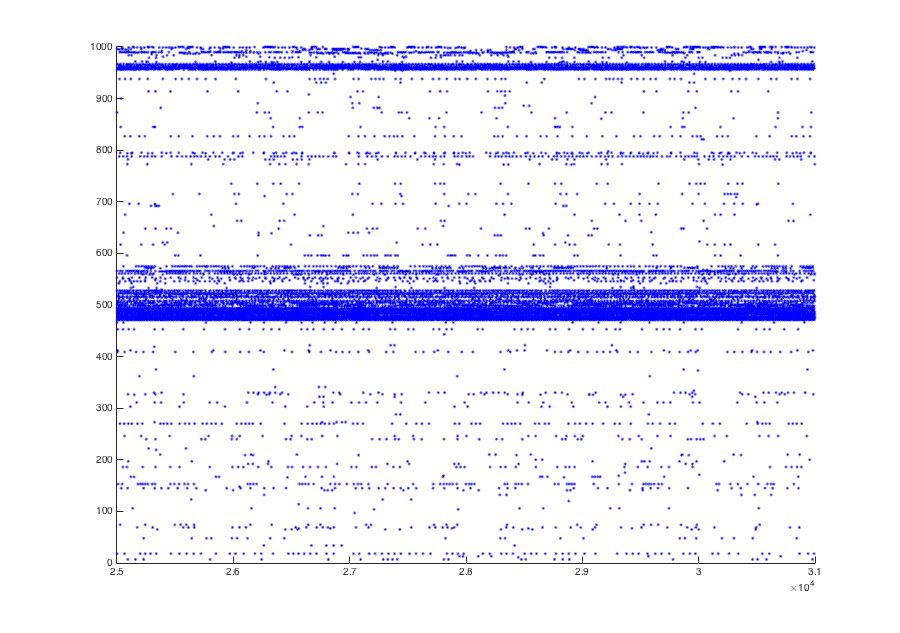
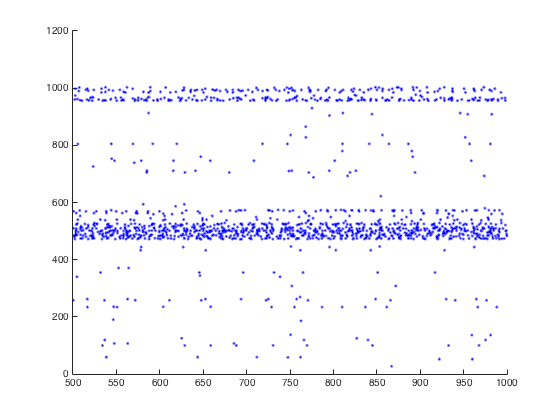 To reproduce Figure 3B, one would need to run the simulation for 31
seconds instead of 1 seconds (set SimTim to 31000 in line 24 and
T_skip to 1000 in line 25 of "RunIDNet.m") and plot the final six
seconds. This takes much longer than the 1 second simulation, of
course. These parameters can be changed in the script, as well as a
number of others which are often varied. The Fig 3B simulation should
resemble this:
To reproduce Figure 3B, one would need to run the simulation for 31
seconds instead of 1 seconds (set SimTim to 31000 in line 24 and
T_skip to 1000 in line 25 of "RunIDNet.m") and plot the final six
seconds. This takes much longer than the 1 second simulation, of
course. These parameters can be changed in the script, as well as a
number of others which are often varied. The Fig 3B simulation should
resemble this:
 How to compute the other measures in Figure 3 are described in the
Methods section of the paper. Most of them are rather elementary (mean
ISI and CV are just the average interspike intervals and its standard
deviation divided by the mean, respectively, for each neuron). Only
the CC (cross correlation) is more involved, its computation is
described in Quiroga-Lombard et al. 2013 (cited in the paper). The
software for computing them is also publically available, the link can
be found in the paper.
All other parameters are defined in 'ConfigIDNet.m' and stored in a
common structure 'SimPar'. In 'IDNetSim.m', parameters specified by
distributions are randomly drawn and the actual simulation program
'IDNet.c' is run as a MEX file. The C code is compiled at the
beginning of 'RunIDNet.m', this line can be commented out after the
first run. The program generates a large number of temporary files
ending with '.dat', which are deleted after the results are stored in
the output file.
The simulation produces a spike train STMtx for all simulated neurons
as well as more detailed variables such as the membrane potential V for
those neurons specified in the parameter 'ViewList'. Finally, it uses
STMtx to draw a raster plot of the spike times.
If model parameters are changed that affect the postsynaptic potential
(PSP) that is elicited in any neuron type by a given synaptic peak
conductance (gmax), the script 'Run_update_inv_con_PSP.m' needs to be
run after making a number of changes to the code that are described in
that script. The results are used to change the parameters of the
function 'inv_con_PSP.m' in the way that is also described in the script.
For questions or comments please contact:
Dr Joachim Hass (joachim.hass@zi-mannheim.de)
or
Prof Daniel Durstewitz (daniel.durstewitz@zi-mannheim.de)
Dept. Theoretical Neuroscience, Bernstein-Center for Computational
Neuroscience, Central Institute of Mental Health, Medical Faculty
Mannheim of Heidelberg University, Mannheim, Germany
Copyright (C) 2016 for all software in this package by the Authors of
the above cited paper. This software may be used under the terms of the
General Public License (www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.txt).
How to compute the other measures in Figure 3 are described in the
Methods section of the paper. Most of them are rather elementary (mean
ISI and CV are just the average interspike intervals and its standard
deviation divided by the mean, respectively, for each neuron). Only
the CC (cross correlation) is more involved, its computation is
described in Quiroga-Lombard et al. 2013 (cited in the paper). The
software for computing them is also publically available, the link can
be found in the paper.
All other parameters are defined in 'ConfigIDNet.m' and stored in a
common structure 'SimPar'. In 'IDNetSim.m', parameters specified by
distributions are randomly drawn and the actual simulation program
'IDNet.c' is run as a MEX file. The C code is compiled at the
beginning of 'RunIDNet.m', this line can be commented out after the
first run. The program generates a large number of temporary files
ending with '.dat', which are deleted after the results are stored in
the output file.
The simulation produces a spike train STMtx for all simulated neurons
as well as more detailed variables such as the membrane potential V for
those neurons specified in the parameter 'ViewList'. Finally, it uses
STMtx to draw a raster plot of the spike times.
If model parameters are changed that affect the postsynaptic potential
(PSP) that is elicited in any neuron type by a given synaptic peak
conductance (gmax), the script 'Run_update_inv_con_PSP.m' needs to be
run after making a number of changes to the code that are described in
that script. The results are used to change the parameters of the
function 'inv_con_PSP.m' in the way that is also described in the script.
For questions or comments please contact:
Dr Joachim Hass (joachim.hass@zi-mannheim.de)
or
Prof Daniel Durstewitz (daniel.durstewitz@zi-mannheim.de)
Dept. Theoretical Neuroscience, Bernstein-Center for Computational
Neuroscience, Central Institute of Mental Health, Medical Faculty
Mannheim of Heidelberg University, Mannheim, Germany
Copyright (C) 2016 for all software in this package by the Authors of
the above cited paper. This software may be used under the terms of the
General Public License (www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.txt).
 To reproduce Figure 3B, one would need to run the simulation for 31
seconds instead of 1 seconds (set SimTim to 31000 in line 24 and
T_skip to 1000 in line 25 of "RunIDNet.m") and plot the final six
seconds. This takes much longer than the 1 second simulation, of
course. These parameters can be changed in the script, as well as a
number of others which are often varied. The Fig 3B simulation should
resemble this:
To reproduce Figure 3B, one would need to run the simulation for 31
seconds instead of 1 seconds (set SimTim to 31000 in line 24 and
T_skip to 1000 in line 25 of "RunIDNet.m") and plot the final six
seconds. This takes much longer than the 1 second simulation, of
course. These parameters can be changed in the script, as well as a
number of others which are often varied. The Fig 3B simulation should
resemble this:
 How to compute the other measures in Figure 3 are described in the
Methods section of the paper. Most of them are rather elementary (mean
ISI and CV are just the average interspike intervals and its standard
deviation divided by the mean, respectively, for each neuron). Only
the CC (cross correlation) is more involved, its computation is
described in Quiroga-Lombard et al. 2013 (cited in the paper). The
software for computing them is also publically available, the link can
be found in the paper.
All other parameters are defined in 'ConfigIDNet.m' and stored in a
common structure 'SimPar'. In 'IDNetSim.m', parameters specified by
distributions are randomly drawn and the actual simulation program
'IDNet.c' is run as a MEX file. The C code is compiled at the
beginning of 'RunIDNet.m', this line can be commented out after the
first run. The program generates a large number of temporary files
ending with '.dat', which are deleted after the results are stored in
the output file.
The simulation produces a spike train STMtx for all simulated neurons
as well as more detailed variables such as the membrane potential V for
those neurons specified in the parameter 'ViewList'. Finally, it uses
STMtx to draw a raster plot of the spike times.
If model parameters are changed that affect the postsynaptic potential
(PSP) that is elicited in any neuron type by a given synaptic peak
conductance (gmax), the script 'Run_update_inv_con_PSP.m' needs to be
run after making a number of changes to the code that are described in
that script. The results are used to change the parameters of the
function 'inv_con_PSP.m' in the way that is also described in the script.
For questions or comments please contact:
Dr Joachim Hass (joachim.hass@zi-mannheim.de)
or
Prof Daniel Durstewitz (daniel.durstewitz@zi-mannheim.de)
Dept. Theoretical Neuroscience, Bernstein-Center for Computational
Neuroscience, Central Institute of Mental Health, Medical Faculty
Mannheim of Heidelberg University, Mannheim, Germany
Copyright (C) 2016 for all software in this package by the Authors of
the above cited paper. This software may be used under the terms of the
General Public License (www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.txt).
How to compute the other measures in Figure 3 are described in the
Methods section of the paper. Most of them are rather elementary (mean
ISI and CV are just the average interspike intervals and its standard
deviation divided by the mean, respectively, for each neuron). Only
the CC (cross correlation) is more involved, its computation is
described in Quiroga-Lombard et al. 2013 (cited in the paper). The
software for computing them is also publically available, the link can
be found in the paper.
All other parameters are defined in 'ConfigIDNet.m' and stored in a
common structure 'SimPar'. In 'IDNetSim.m', parameters specified by
distributions are randomly drawn and the actual simulation program
'IDNet.c' is run as a MEX file. The C code is compiled at the
beginning of 'RunIDNet.m', this line can be commented out after the
first run. The program generates a large number of temporary files
ending with '.dat', which are deleted after the results are stored in
the output file.
The simulation produces a spike train STMtx for all simulated neurons
as well as more detailed variables such as the membrane potential V for
those neurons specified in the parameter 'ViewList'. Finally, it uses
STMtx to draw a raster plot of the spike times.
If model parameters are changed that affect the postsynaptic potential
(PSP) that is elicited in any neuron type by a given synaptic peak
conductance (gmax), the script 'Run_update_inv_con_PSP.m' needs to be
run after making a number of changes to the code that are described in
that script. The results are used to change the parameters of the
function 'inv_con_PSP.m' in the way that is also described in the script.
For questions or comments please contact:
Dr Joachim Hass (joachim.hass@zi-mannheim.de)
or
Prof Daniel Durstewitz (daniel.durstewitz@zi-mannheim.de)
Dept. Theoretical Neuroscience, Bernstein-Center for Computational
Neuroscience, Central Institute of Mental Health, Medical Faculty
Mannheim of Heidelberg University, Mannheim, Germany
Copyright (C) 2016 for all software in this package by the Authors of
the above cited paper. This software may be used under the terms of the
General Public License (www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.txt).