Read me text to use the Integrate-and-fire fitting toolbox.
The fitting procedure implemented here is described in detail in the
following paper:
Extraction and Classification of Three Cortical Neuron Types Reveals
Two Distinct Adaptation Mechanisms
Skander Mensi, Richard Naud, Christian Pozzorini, Michael Avermann,
Carl C.H. Petersen, and Wulfram Gerstner
Journal of NeuroPhysiology, 2011
Utilization, simply run the script fit_IF() on the matlab prompt:
fit_IF()
This script, fit stochastic IF model with spike-triggered current eta
and moving threshold gamma as described by Eq 1-3, using a voltage
traces V and the injected current I. Here the fitting procedure is
applied on surrogate data generated with the same model used for
fitting. This is done to highlight the performance of our fitting
method by evaluating the error done on the estimation of the reference
parameters. The reference parameters somehow reflects parameters
estimated on in-vitro recordings.
The model reference and the fitted model is described by Eq:
C(V_dot(t)) = -g_l(V(t)-E_l) + I(t) + sum_(t_hat)(eta(t-t_hat))
lambda(t) = lambda_0 exp(V(t) - ((V_0 +
sum_(t_hat)gamma(t-t_hat))/Delta_V)
If spike: V <- E_reset
t = t + t_refr
t <- t_hat
The main steps of the fitting procedure are:
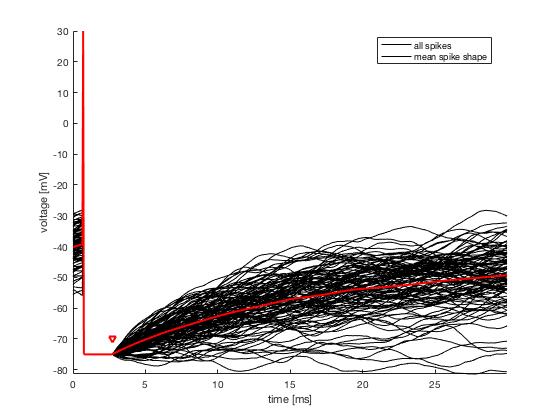
1. Extract Spike Shape, absolute refractory period T_refr and
corresponding voltage reset E_reset from V
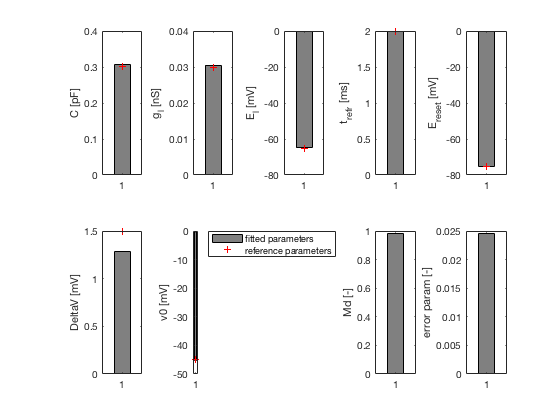
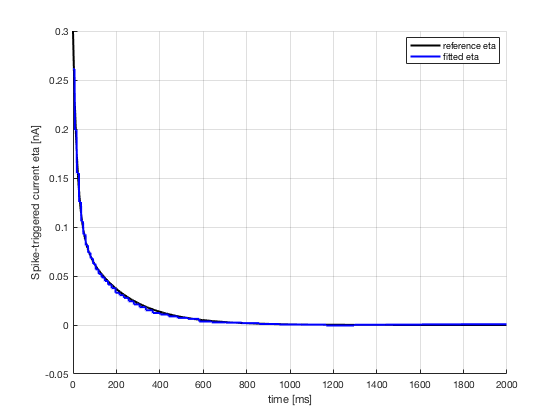
2. Estimate optimal spike-triggered current eta(t) and passive
parameters, C, G_l and E_l with linear regression
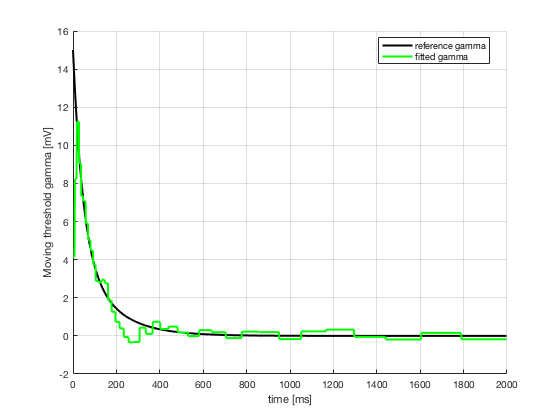
3. Estimate moving threshold gamma(t) by maximizing log-likelihood of
the observed spike train
4. Estimate performance of the fitted model on new data set (test
set).
5. Plot results
This script produce 5 figures:
1. Spike Shape with T_refr and E_reset
 2. passive parameters
2. passive parameters
 3. eta(t)
3. eta(t)
 3. gamma(t)
3. gamma(t)
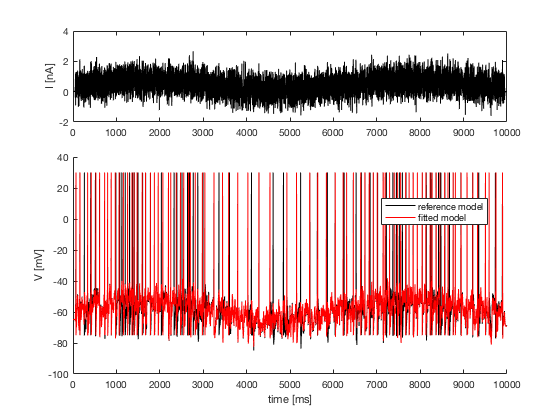
 4. predicted voltage traces and data voltage traces
4. predicted voltage traces and data voltage traces
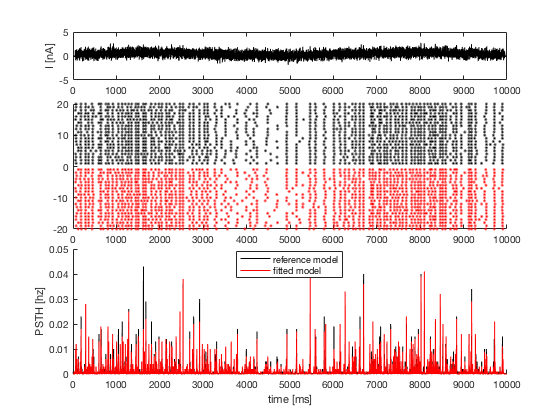
 5. raster plot and PSTH
5. raster plot and PSTH
 The script can be easily modified to estimated parameters from
intracellular recordings. In this case, the user has to replace I and
V by the injected current (in nA) and the recorded voltage in mV. Then
the user has to check the following parameters to ensure that the
fitting goes properly:
1. be sure that the spikes are well detected (here spike times are set
to the maximum value (in a 1ms window), following upward
zero-crossing.
2. Double check the estimated t_refr and E_reset (i.e. in this simple
implementation of the fitting procedure, t_refr is set to the time
after the spike onset, where the minimal value of the spike shape is
reached and E_reset is set to the value of this minima. However,
depending on the cell type, the spike shape does not necessary exhibit
a local minimum following a spike, in this, the user has to set t_refr
to a reasonable value and then E_reset to the value of the mean
voltage at this time.)
3. choose an appropriate value to set the onset of the spikes (as
mentioned in 1., the spike times are set to the maximum value of the
spikes, however to evaluate the threshold one has to consider the time
at which the threshold is crossed with visual heuristics. It is
possible to use figure 1 to choose the exact value of delay).
4. the parameters delay is used two times with different value, ones
for the extraction of eta and ones for the estimation of gamma, be
sure to use an appropriate value for each step. Note: for eta the
exact value of delay is note critical as soon as it removes completely
the spike shape (for instance 2 or 3 ms before the maximum value of
the spike), whereas the value of delay is highly critical to estimate
gamma, since it sets the voltage at which a spike is emitted.
WARNING: the fitting procedure is fast but requires high memory during
the linear regression (matrix inversion). The longer part of the
script is the performance evaluation, because one has to generate 1000
spike trains from the reference model and 1000 spike trains from the
fitted model to evaluate Md. If to long, one can reduce the duration
of the stimuli for the test set (30 seconds) or the number of
repetitions (1000) used to compute the PSTH. On a Mac book pro 2.3
GHz with 4 Go RAM, execution time is: 3 minutes
CONTACT: For any question or remark on the code contact:
skander.mensi@epfl.ch
Copyright Skander Mensi 2011
The script can be easily modified to estimated parameters from
intracellular recordings. In this case, the user has to replace I and
V by the injected current (in nA) and the recorded voltage in mV. Then
the user has to check the following parameters to ensure that the
fitting goes properly:
1. be sure that the spikes are well detected (here spike times are set
to the maximum value (in a 1ms window), following upward
zero-crossing.
2. Double check the estimated t_refr and E_reset (i.e. in this simple
implementation of the fitting procedure, t_refr is set to the time
after the spike onset, where the minimal value of the spike shape is
reached and E_reset is set to the value of this minima. However,
depending on the cell type, the spike shape does not necessary exhibit
a local minimum following a spike, in this, the user has to set t_refr
to a reasonable value and then E_reset to the value of the mean
voltage at this time.)
3. choose an appropriate value to set the onset of the spikes (as
mentioned in 1., the spike times are set to the maximum value of the
spikes, however to evaluate the threshold one has to consider the time
at which the threshold is crossed with visual heuristics. It is
possible to use figure 1 to choose the exact value of delay).
4. the parameters delay is used two times with different value, ones
for the extraction of eta and ones for the estimation of gamma, be
sure to use an appropriate value for each step. Note: for eta the
exact value of delay is note critical as soon as it removes completely
the spike shape (for instance 2 or 3 ms before the maximum value of
the spike), whereas the value of delay is highly critical to estimate
gamma, since it sets the voltage at which a spike is emitted.
WARNING: the fitting procedure is fast but requires high memory during
the linear regression (matrix inversion). The longer part of the
script is the performance evaluation, because one has to generate 1000
spike trains from the reference model and 1000 spike trains from the
fitted model to evaluate Md. If to long, one can reduce the duration
of the stimuli for the test set (30 seconds) or the number of
repetitions (1000) used to compute the PSTH. On a Mac book pro 2.3
GHz with 4 Go RAM, execution time is: 3 minutes
CONTACT: For any question or remark on the code contact:
skander.mensi@epfl.ch
Copyright Skander Mensi 2011
 2. passive parameters
2. passive parameters
 3. eta(t)
3. eta(t)
 3. gamma(t)
3. gamma(t)
 4. predicted voltage traces and data voltage traces
4. predicted voltage traces and data voltage traces
 5. raster plot and PSTH
5. raster plot and PSTH
 The script can be easily modified to estimated parameters from
intracellular recordings. In this case, the user has to replace I and
V by the injected current (in nA) and the recorded voltage in mV. Then
the user has to check the following parameters to ensure that the
fitting goes properly:
1. be sure that the spikes are well detected (here spike times are set
to the maximum value (in a 1ms window), following upward
zero-crossing.
2. Double check the estimated t_refr and E_reset (i.e. in this simple
implementation of the fitting procedure, t_refr is set to the time
after the spike onset, where the minimal value of the spike shape is
reached and E_reset is set to the value of this minima. However,
depending on the cell type, the spike shape does not necessary exhibit
a local minimum following a spike, in this, the user has to set t_refr
to a reasonable value and then E_reset to the value of the mean
voltage at this time.)
3. choose an appropriate value to set the onset of the spikes (as
mentioned in 1., the spike times are set to the maximum value of the
spikes, however to evaluate the threshold one has to consider the time
at which the threshold is crossed with visual heuristics. It is
possible to use figure 1 to choose the exact value of delay).
4. the parameters delay is used two times with different value, ones
for the extraction of eta and ones for the estimation of gamma, be
sure to use an appropriate value for each step. Note: for eta the
exact value of delay is note critical as soon as it removes completely
the spike shape (for instance 2 or 3 ms before the maximum value of
the spike), whereas the value of delay is highly critical to estimate
gamma, since it sets the voltage at which a spike is emitted.
WARNING: the fitting procedure is fast but requires high memory during
the linear regression (matrix inversion). The longer part of the
script is the performance evaluation, because one has to generate 1000
spike trains from the reference model and 1000 spike trains from the
fitted model to evaluate Md. If to long, one can reduce the duration
of the stimuli for the test set (30 seconds) or the number of
repetitions (1000) used to compute the PSTH. On a Mac book pro 2.3
GHz with 4 Go RAM, execution time is: 3 minutes
CONTACT: For any question or remark on the code contact:
skander.mensi@epfl.ch
Copyright Skander Mensi 2011
The script can be easily modified to estimated parameters from
intracellular recordings. In this case, the user has to replace I and
V by the injected current (in nA) and the recorded voltage in mV. Then
the user has to check the following parameters to ensure that the
fitting goes properly:
1. be sure that the spikes are well detected (here spike times are set
to the maximum value (in a 1ms window), following upward
zero-crossing.
2. Double check the estimated t_refr and E_reset (i.e. in this simple
implementation of the fitting procedure, t_refr is set to the time
after the spike onset, where the minimal value of the spike shape is
reached and E_reset is set to the value of this minima. However,
depending on the cell type, the spike shape does not necessary exhibit
a local minimum following a spike, in this, the user has to set t_refr
to a reasonable value and then E_reset to the value of the mean
voltage at this time.)
3. choose an appropriate value to set the onset of the spikes (as
mentioned in 1., the spike times are set to the maximum value of the
spikes, however to evaluate the threshold one has to consider the time
at which the threshold is crossed with visual heuristics. It is
possible to use figure 1 to choose the exact value of delay).
4. the parameters delay is used two times with different value, ones
for the extraction of eta and ones for the estimation of gamma, be
sure to use an appropriate value for each step. Note: for eta the
exact value of delay is note critical as soon as it removes completely
the spike shape (for instance 2 or 3 ms before the maximum value of
the spike), whereas the value of delay is highly critical to estimate
gamma, since it sets the voltage at which a spike is emitted.
WARNING: the fitting procedure is fast but requires high memory during
the linear regression (matrix inversion). The longer part of the
script is the performance evaluation, because one has to generate 1000
spike trains from the reference model and 1000 spike trains from the
fitted model to evaluate Md. If to long, one can reduce the duration
of the stimuli for the test set (30 seconds) or the number of
repetitions (1000) used to compute the PSTH. On a Mac book pro 2.3
GHz with 4 Go RAM, execution time is: 3 minutes
CONTACT: For any question or remark on the code contact:
skander.mensi@epfl.ch
Copyright Skander Mensi 2011