This is the readme for the model associated with the paper:
Poleg-Polsky A, Diamond JS, 2011 Imperfect Space Clamp Permits
Electrotonic Interactions between Inhibitory and Excitatory Synaptic
Conductances, Distorting Voltage Clamp Recordings. PLoS ONE 6(4):
e19463. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019463
This simulation examines the accuracy of the voltage clamp technique
in detecting the excitatory and the inhibitory components of the
synaptic drive.
TO RUN THE SIMULATION
(First auto-launch from ModelDB, or download and extract the archive
and then compile the mod files with nrnivmodl (unix), mknrndll
(mswin), or drag and dropping archive folder onto mknrndll (mac)).
To run the simulation press the "run" button on the control panel.
To change the excitatory synaptic conductances set the "AMPA" and the
"NMDA" values (default are 0.5 and 0.2 nS)
To set the inhibitory conductance change the "Amp" value under
"Inhibition". "Tau" changes the decay time constant of the inhibitory
synapse.
The "Hol determines the holding potential of the voltage clamp.
The "batchrun" button executes multiple runs at holding potentials
between -100 and 20mV
GRAPHS
Graph[0] and [4]-somatic (and dendritic) voltage
Graph[1] excitatory (ge) and inhibitory (gi) conductances
Graph[2] excitatory (ie) and inhibitory (ii) currents
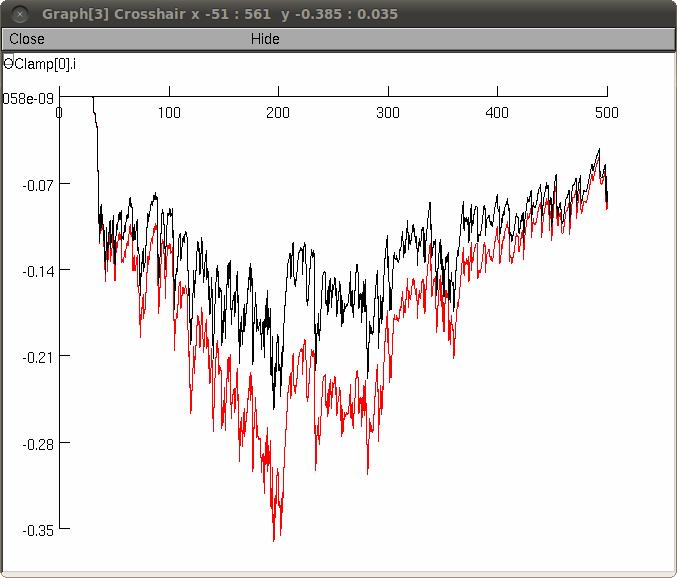
Graph[3] the current recorded by the voltage clamp electrode
EXAMPLE
Figure1 (below) shows the current recorded by the somatic electrode during
execution of the simulation at a holding potential of -60mV with
excitation and inhibition (black) and excitation alone (red). The
inhibitory drive, though "clamped" at its reversal potential had a
significant influence on the recording.
 20110511 ModelDB Administrator: globalRa (Ra=100) update was added to
end of vccell.hoc
20110511 ModelDB Administrator: globalRa (Ra=100) update was added to
end of vccell.hoc
 20110511 ModelDB Administrator: globalRa (Ra=100) update was added to
end of vccell.hoc
20110511 ModelDB Administrator: globalRa (Ra=100) update was added to
end of vccell.hoc
20110511 ModelDB Administrator: globalRa (Ra=100) update was added to end of vccell.hoc